What is the Power Plant?
A power plant is generally a power generating plant or the station that is used for the generation of electric power on a large scale, usually in the order of KW or MW. These power plants are generally located in suburban areas which are generally far from cities or load centers. It is because a power plant requires a huge land area and water resources supply. In general, the power plant is in that area where the river is flowing and has a regular supply of water, waste disposal facilities, and transportation facilities.
Working of Hydroelectric Power Plant
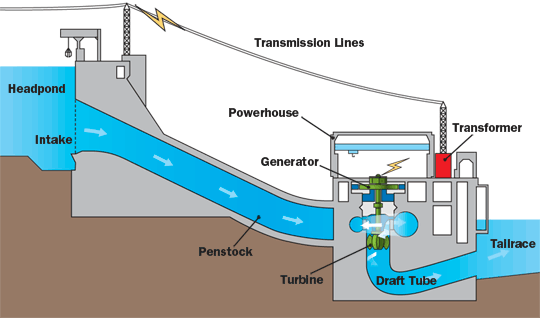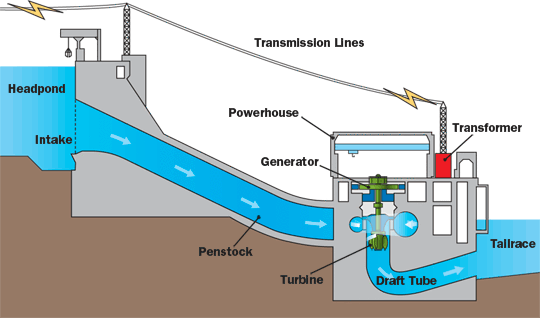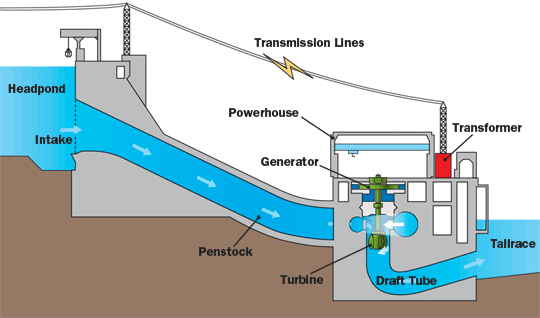
The reservoir and dam are built to store the water from the running river. The dam is mainly built to provide sufficient water head as per load requirements. The water from the dam through the penstock pipe and nozzle is allowed to impinge on the turbine bucket or vane/blade depending on the type of turbines, which in turn causes rotation of the turbine shaft.
The turbine shaft is connected to the generator; therefore generator shaft also rotates along with the turbine shaft. The water after rotating the turbine shaft goes to the tailrace with high pressure and gets mixed into the Downside River or pond.
The principle is that the potential energy of water at rest in a dam is converted into kinetic energy in penstock pipe and in pressure energy at the nozzle outlet. These kinetic and pressure energy together rotated the turbine blades and created conversion into mechanical energy. And that turbine rotating shaft is coupled with the generator; it generated electrical energy when rotation happens.
Gross Head
The gross head is the difference between the headrace and tailrace.
Net Head
Net head is the actual head that water can obtain. Net head is always less than the gross head. The reason is that there is always some friction, bending, and turbulence present in the path. Head losses due to the kinetic energy are remained in the water and were not used by the turbine. That heat loss is determined as h2=v2/2g where v is the velocity of water at the tailrace and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Merits of Hydroelectric Power Plant
- Fuel is eliminated, therefore low operating costs.
- Long plant life usually 50 to 100 years.
- Few workers are sufficient for operation management.
- No greenhouse gas emission.
- A plant can be easily started and closed.
- The hydroelectric power plant can be utilized for irrigation, flood control, and also for tourism.
Demerits of Hydroelectric Power Plants
- The area in which power plant is made may disrupt many people’s life and environment.
- The initial investment cost is very high.
- Power generation is not the same throughout the year.
- The project duration is long.
- There is always a kind scare in mind related to any uncertain happenings such as flood, life loss, and property loss because of dam auto bombardment.
Major Components of Hydroelectric power plant
Some major components of hydroelectric power plants are Dam, Water reservoir, Gate, Spillway, Surge tank, Pressure tunnel or Canal, Penstock, Water turbine, Draft tube, Tailrace, and Powerhouse.
Dam
The main purpose of the dam is to store the water, increase the heat when necessary, and control the flow of water to the penstock with the help of gates installed in the dam. A dam is made at such a place where the land is strong and should be able to withstand reservoir water load.
Water reservoir
During the rainy season, there is lots of water that need to be stored so that that water can be used during the off-season for power generation. In the reservoir, the level of the surface of the water is called the headwater level.
Gate
The main purpose of the gate is used to control the flow of water from the dam.
Spillway
During the rainy season, there is a huge amount of water gets collected into the reservoir. At that time, spillway comes into action and allows the water to another safe reservoir. The spillway prevents the dam from any accidents.
Surge tank
It is a small tank or a reservoir in which the water level falls or rises due to sudden pressure change. It is provided to prevent water hammering in penstock pipes due to unbalanced water pressure.
Pressure tunnel or canal
The pressure tunnel or canal is a close conduit that allows the water to flow to the penstock in a smooth path. The construction cost of this pressure canal is relatively high.
Penstock
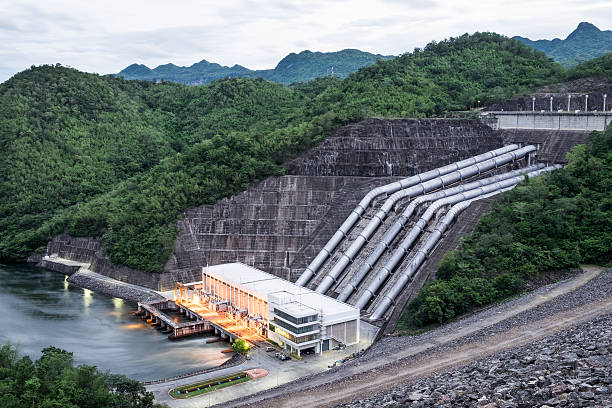

The main aim of the penstock is to bring water from a dam to the turbine. The penstock is usually provided for a high head plant. That is, a plant having its dam located 250m above from its turbine location. The penstock helps to increase the velocity of the water and the made to strike on the turbine blade through the nozzle.
Water turbine
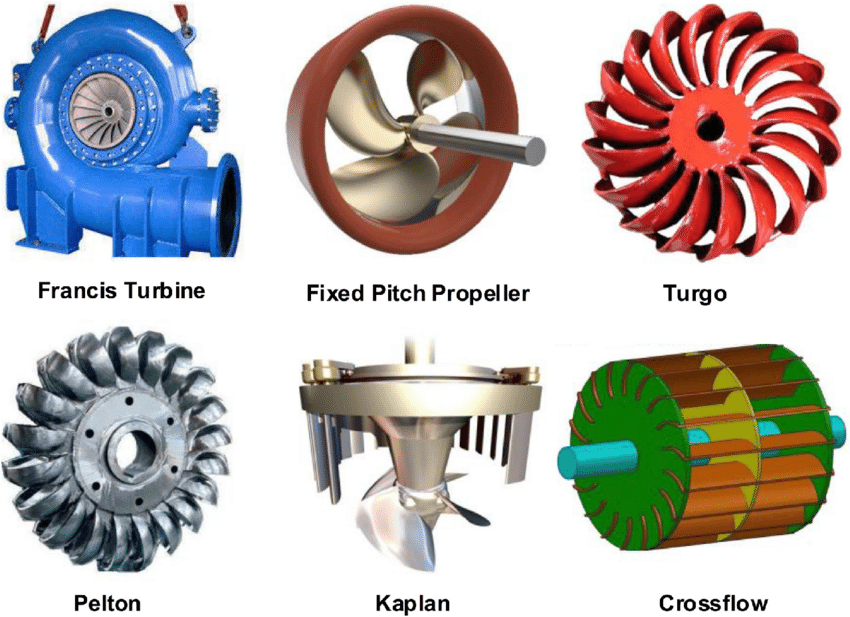
The water turbine is also known as a hydraulic turbine. This turbine converts the energy of water into mechanical energy. The water turbine’s main function is to use the water to rotate its shaft. As the shaft of the water turbine is coupled with a generator, the generator shaft also rotates together. We knew that a generator has a magnet and conductor inside its configuration. When there is a relation motion between them, the electricity is produced.
Draft tube
It is a device that is linked at the exit of Francis and Kaplan’s reaction turbine. It converts the Kinetic energy of water coming out from the turbine into pressure energy. The draft tube is a conical shape object and it has two sections. The first is smaller which is connected to the exit of the turbine and the other is the wider section which is submerged into the tailrace. The wider section is submerged into tailrace water in other to create suction pressure so that the turbine works properly.
Tailrace
It is the path that exit water follows when it comes out of the draft tube. The surface water level is said as tailrace water level.
Powerhouse
You may also like:







